The Earth, our home planet, is a complex and dynamic system that has fascinated scientists and explorers for centuries. From the depths of the oceans to the highest mountain peaks, our planet is a treasure trove of natural wonders and mysteries waiting to be unravelled.
One of the most transformative advancements in Earth Science in recent years has been the use of satellite technology to observe and study our planet from space. Satellites have revolutionized our understanding of Earth, providing unprecedented insights into its geology, weather patterns, climate change, natural resources, and environmental health.
Hello friends, I am Uzaif Kevin the author of your own website uzfkvn.com I hope you all are absolutely fine. I’m fine too. So without wasting time, In this Article I will tell you “we will explore how satellite technology has transformed Earth Science, revolutionizing our understanding of our planet and shaping our approach to environmental conservation and sustainability.”
Soo Lets Begin,
Satellites, often launched into space by national space agencies or private entities, are sophisticated instruments that orbit the Earth, collecting data and images from a vantage point that is not possible from the ground.
These satellite observations enable scientists to study the Earth on a global scale, capturing data over large areas and long periods of time, and providing a wealth of information that is used to make informed decisions and policies related to Earth Science.
One of the key areas where satellites have made significant contributions is in the study of geology. Geologists use satellite images to map the Earth’s surface, identify different rock types, and study geological formations.
For example, satellite images can reveal the distribution of different types of rocks, such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and provide insights into the processes that formed them. Satellite data can also help identify potential mineral and energy resources, such as oil and gas reserves, ores, and groundwater resources, which are critical for our modern society.
Satellites have revolutionized our understanding of weather patterns and climate change. Meteorological satellites constantly monitor the Earth’s atmosphere, providing real-time data on temperature, pressure, humidity, wind patterns, and precipitation.
This data is used to create weather forecasts, track the paths of hurricanes, and monitor other severe weather events, helping to mitigate their impacts and save lives. Satellite data also contributes to our understanding of climate change, as it provides long-term records of weather patterns and helps track changes in the Earth’s climate system over time.
This data is essential for climate modeling and predicting future climate scenarios, which are crucial for developing strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Satellites are also critical for studying the Earth’s oceans, which cover more than 70% of the planet’s surface. Oceanographic satellites provide data on sea surface temperature, sea level, ocean currents, and the distribution of marine life, among other parameters.

This data is used to study ocean dynamics, such as ocean circulation patterns, and the impacts of climate change on the world’s oceans, including sea level rise and changes in marine ecosystems.
Satellite data also helps in the monitoring and management of marine resources, such as fisheries, coral reefs, and coastal zones, contributing to sustainable ocean governance and conservation efforts.
Another significant contribution of satellite technology to Earth Science is in the field of environmental conservation. Satellites provide critical data for monitoring and managing natural resources, tracking changes in land cover, deforestation, and ecosystem health.
For example, satellite data is used to monitor protected areas, detect illegal logging or mining activities, and assess the health of forests, wetlands, and other ecosystems. This information is essential for developing strategies for biodiversity conservation, habitat restoration, and sustainable resource management, helping to protect our planet’s precious natural heritage.
Satellite technology has also been instrumental in disaster monitoring and management. Satellites can quickly assess the extent and impacts of natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and wildfires, providing critical information for emergency response and disaster relief efforts.
Satellite images can help identify affected areas, assess damages, and monitor changes in real-time, enabling authorities to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively. For example, during wildfires, satellites can detect hotspots and track the spread of fires, helping firefighting efforts and evacuation planning.

During hurricanes and tsunamis, satellites can track storm movements, measure sea surface temperatures, and provide early warning systems, saving lives and minimizing damage.
Satellites have also revolutionized our understanding of air quality and pollution monitoring. Satellites equipped with sensors that measure atmospheric composition can provide data on pollutants such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, helping to monitor air quality and understand the sources and impacts of air pollution.
This information is used to develop strategies for air pollution control, emission reduction, and public health protection, contributing to efforts to improve air quality and combat climate change.
Satellite technology has also enabled us to study the Earth’s climate history by examining ice cores, which are long cylinders of ice extracted from polar ice caps. These ice cores contain information about the Earth’s climate history dating back thousands of years, including changes in temperature, greenhouse gas concentrations, and atmospheric conditions.
Satellite data, such as measurements of ice thickness and movement, can help identify potential locations for ice core drilling and provide valuable information to reconstruct past climate changes and understand the Earth’s climate system dynamics.
Satellites also play a crucial role in communication, navigation, and monitoring of human activities on Earth. Communication satellites provide global connectivity, enabling worldwide internet access, television broadcasting, and telecommunications. Navigation satellites, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), provide precise positioning, timing, and navigation services that are used in various applications, including transportation, agriculture, and disaster response.
Monitoring satellites can also help detect changes in human activities, such as urbanization, deforestation, agriculture, and infrastructure development, providing valuable information for urban planning, land management, and sustainable development.
Despite the many benefits of satellite technology in Earth Science, there are also challenges and limitations. Satellite data can be expensive to acquire, process, and analyze, and may require significant technical expertise and infrastructure. There are also limitations in satellite sensor capabilities, such as resolution, accuracy, and sensitivity, which may affect the quality and reliability of the data obtained.
There are concerns about data privacy, security, and the ethical use of satellite data, including issues related to surveillance, discrimination, and unequal access to data.
In conclusion, satellite technology has revolutionized Earth Science, providing unprecedented insights into our planet and transforming our understanding of its geology, weather patterns, climate change, natural resources, and environmental health. Satellites have enabled scientists to study the Earth on a global scale, capturing data and images from space that would not be possible from the ground.
Satellite data has been crucial in advancing our knowledge in various fields, including geology, meteorology, oceanography, environmental conservation, disaster management, air quality monitoring, climate history, communication, navigation, and monitoring of human activities.
There are also challenges and limitations in the use of satellite data, and it is essential to address them to ensure responsible and equitable use of this technology for the benefit of humanity and our planet.
In conclusion, satellite technology has revolutionized our understanding of Earth, providing a new perspective from space that has transformed the field of Earth Science. Satellites have provided us with a wealth of data and insights that have advanced our knowledge in various areas, from geology and meteorology to environmental conservation and disaster management.
With ongoing advancements in satellite technology and data processing capabilities, we can expect further breakthroughs in Earth Science and continue to explore the wonders of our planet from space, unlocking its mysteries and addressing new challenges.
As technology continues to evolve, satellites are becoming more sophisticated, with improved sensors, higher resolution images, and enhanced data processing capabilities. These advancements are expanding the scope of Earth Science research and opening up new possibilities for studying our planet in even greater detail.
One area where satellites have been particularly transformative is in studying climate change. Satellite data has been crucial in monitoring and measuring changes in the Earth’s climate system, including changes in temperature, sea level, ice cover, and greenhouse gas concentrations.
Satellites equipped with advanced sensors can provide continuous monitoring of key climate variables, helping scientists to track and understand the impacts of climate change on our planet.
For example, satellite data has shown that the Arctic sea ice extent has been declining rapidly over the past few decades, contributing to rising sea levels and changes in global climate patterns. Satellites have also been used to measure changes in vegetation, which can be an indicator of climate change impacts on ecosystems and agriculture.
Satellites have also been instrumental in monitoring natural disasters, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. Satellite data can provide early warning systems and enable rapid response to disasters, helping to mitigate their impacts and save lives.
For example, satellites can track the movement and intensity of hurricanes, providing crucial information for evacuation planning and emergency response. Satellites can also detect changes in ground deformation and thermal anomalies, which can indicate volcanic eruptions or earthquake activity, helping authorities to issue warnings and evacuate affected areas.
Satellites are also invaluable in monitoring and managing Earth’s natural resources, including forests, water resources, and fisheries. Satellites equipped with remote sensing instruments can detect changes in forest cover, monitor deforestation and degradation, and assess the health and productivity of forests.
This information is vital for conservation efforts, sustainable forest management, and biodiversity protection. Satellites can also measure changes in water resources, such as river flow, lake levels, and groundwater storage, helping to manage water scarcity, monitor droughts, and plan for water allocation.
Satellites can monitor fishing activities, such as vessel movements and fishing gear deployment, helping to combat illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing and promote sustainable fisheries management.
Satellite technology also plays a crucial role in disaster management and emergency response. During natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods, satellites can provide critical information for emergency response and disaster relief efforts. Satellite images can help identify affected areas, assess damages, and monitor changes in real-time, enabling authorities to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
For example, during wildfires, satellites can detect hotspots and track the spread of fires, helping firefighting efforts and evacuation planning. During hurricanes and tsunamis, satellites can track storm movements, measure sea surface temperatures, and provide early warning systems, saving lives and minimizing damage.
Satellite technology has also enabled us to study the Earth’s climate history by examining ice cores, which are long cylinders of ice extracted from polar ice caps. These ice cores contain information about the Earth’s climate history dating back thousands of years, including changes in temperature, greenhouse gas concentrations, and atmospheric conditions.
Satellite data, such as measurements of ice thickness and movement, can help identify potential locations for ice core drilling and provide valuable information to reconstruct past climate changes and understand the Earth’s climate system dynamics.
Satellites also play a crucial role in communication, navigation, and monitoring of human activities on Earth. Communication satellites provide global connectivity, enabling worldwide internet access, television broadcasting, and telecommunications.
Navigation satellites, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), provide precise positioning, timing, and navigation services that are used in various applications, including transportation, agriculture, and disaster response. Monitoring satellites can also help detect changes in human activities, such as urbanization, deforestation, industrial activities, and pollution.
For example, satellites can monitor changes in urban areas, track expansion of cities, and monitor changes in land use and land cover, providing valuable information for urban planning, infrastructure development, and environmental management.
Satellites can also monitor industrial activities, such as mining, oil and gas exploration, and transportation, helping to assess their environmental impacts and support sustainable resource management.
Satellites equipped with sensors that can detect air pollution, such as particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide, can provide critical information on air quality, helping to monitor pollution sources, assess health risks, and support environmental policies.
Satellites are also playing a significant role in disaster preparedness and risk reduction. Satellite data can provide valuable information for vulnerability assessments, hazard mapping, and risk modeling. By analyzing satellite data, scientists and policymakers can identify areas at high risk of natural disasters, such as landslides, floods, and earthquakes, and develop strategies for disaster preparedness and response.
For example, satellites can provide data on terrain elevation, land cover, and precipitation patterns, which can be used to model flood risks and develop early warning systems. Satellite data can also help identify potential landslide-prone areas by monitoring changes in land surface conditions, such as ground deformation and soil moisture.
Satellites have been utilized in tracking and monitoring wildlife populations, including endangered species, providing critical information for conservation efforts. Satellites equipped with high-resolution cameras can capture images of wildlife habitats, track animal movements, and monitor changes in biodiversity hotspots.
This information helps scientists and conservationists understand wildlife behavior, population dynamics, and habitat changes, which are crucial for effective conservation planning and management. Satellites have been used to track wildlife migrations, monitor the movements of marine mammals, and study changes in bird populations, providing valuable insights into their ecology and behavior.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in satellite technology for monitoring and managing the impacts of climate change on agriculture and food security. Satellites can provide information on crop health, soil moisture, temperature, and precipitation, helping farmers to optimize crop management practices, monitor droughts, and predict crop yields.
This information can be used to enhance agricultural productivity, reduce risks associated with weather extremes, and support sustainable agricultural practices. Satellite data can also help monitor changes in land use, such as deforestation and conversion of natural habitats to agricultural land, which can impact biodiversity, carbon storage, and ecosystem services.
In conclusion, satellite technology has revolutionized our understanding of Earth and its complex systems. Satellites have become indispensable tools for Earth Science research, providing invaluable data for studying climate change, natural disasters, natural resources, human activities, wildlife populations, and agriculture.
Satellites have enabled us to monitor and understand changes in our planet on a global scale and have contributed to addressing environmental challenges and supporting sustainable development.
As technology continues to advance, satellites are expected to play an even more significant role in Earth observation and provide critical information for addressing pressing global issues, such as climate change, disaster management, and food security. With continued investment and innovation, satellite technology will continue to be a vital asset in our quest to understand and protect our planet, Earth.

Table of Contents
What is the definition of Earth Science?
Earth Science, also known as geoscience, is a scientific field that studies the physical and chemical processes that shape the Earth and its environments.
It is an interdisciplinary field that combines knowledge from various scientific disciplines, including geology, meteorology, oceanography, astronomy, and environmental science, to understand the Earth’s composition, structure, history, and dynamics.
Earth Science encompasses the study of the Earth’s atmosphere, hydrosphere (oceans, lakes, and rivers), geosphere (rock, soil, and minerals), and biosphere (living organisms), and how these systems interact and influence each other.
It involves the investigation of natural processes such as weathering, erosion, volcanism, plate tectonics, climate change, and the formation of rocks and minerals, as well as human interactions with the Earth, such as resource extraction, pollution, and environmental management.
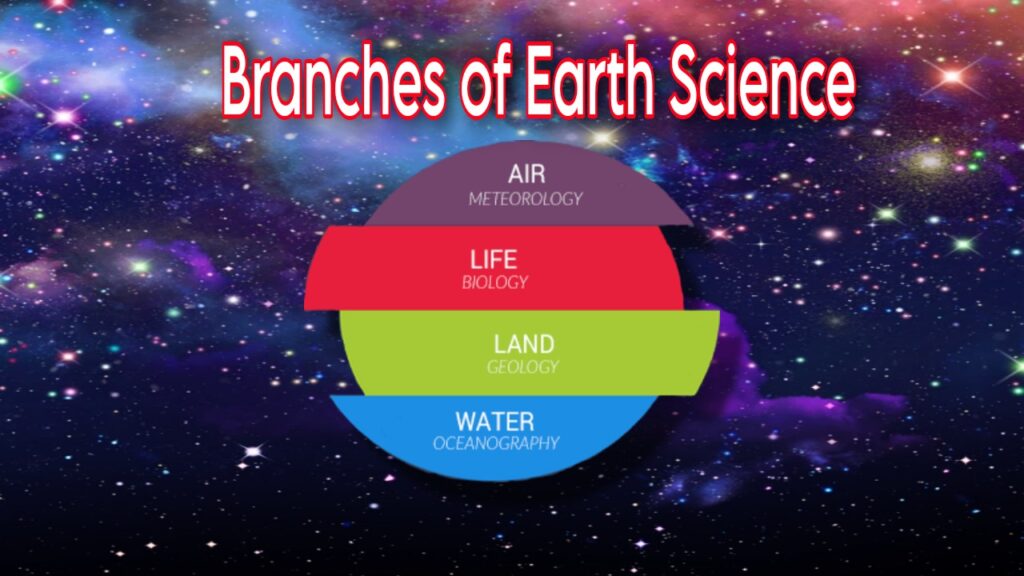
How many branches of Earth Science?
Earth Science, or geoscience, is a broad field that encompasses several branches or sub-disciplines, each focusing on different aspects of the Earth and its systems. Some of the main branches of Earth Science include:
- Geology: Geology is the study of the Earth’s composition, structure, history, and processes related to the formation and evolution of rocks, minerals, mountains, and the Earth’s crust. It includes fields such as petrology (study of rocks), mineralogy (study of minerals), geomorphology (study of landforms), stratigraphy (study of rock layers), and structural geology (study of rock deformation).
- Meteorology: Meteorology is the study of the Earth’s atmosphere and weather patterns, including the study of temperature, pressure, humidity, precipitation, wind, and other atmospheric phenomena. Meteorologists study weather patterns, weather forecasting, climate modeling, and the impacts of weather on human activities and the environment.
- Oceanography: Oceanography is the study of the world’s oceans, including their composition, structure, properties, and processes. It covers various aspects such as physical oceanography (study of physical properties of oceans), chemical oceanography (study of chemical composition of oceans), biological oceanography (study of marine life), and geological oceanography (study of oceanic geology and sediments).
- Astronomy: Although not strictly an Earth Science, astronomy involves the study of celestial objects such as planets, stars, galaxies, and the universe as a whole. It includes fields such as planetary science (study of planets and their moons), astrophysics (study of physical properties and behavior of celestial objects), and cosmology (study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe).
- Environmental Science: Environmental Science is an interdisciplinary field that encompasses the study of the interactions between the Earth’s systems and human activities. It involves understanding the impacts of human activities on the environment, such as pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change, and developing strategies for sustainable resource management and environmental conservation.
These are just a few examples of the branches of Earth Science, and the field is continuously evolving as new research and technologies emerge. Earth Science is an interdisciplinary field that draws from various scientific disciplines to better understand the Earth and its systems, and to address complex environmental challenges facing our planet.

What is the best topic in Earth Science?
The “best” topic in Earth Science can be subjective and dependent on individual interests, career goals, and research priorities.
- Climate Change: Climate change is a critical topic in Earth Science, as it impacts the Earth’s climate system and has far-reaching consequences for the environment, ecosystems, and human societies. The study of climate change involves understanding past and present climate patterns, investigating the causes and mechanisms of climate change, and predicting future climate scenarios using climate models.
- Natural Hazards: Earth Science plays a crucial role in the study of natural hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, hurricanes, and floods. Understanding the underlying geological, atmospheric, and oceanic processes that cause these hazards, and developing strategies for hazard mitigation, preparedness, and response, is an important area of research within Earth Science.
- Geohazards: Geohazards refer to geological processes that pose risks to human activities and infrastructure, such as landslides, rockfalls, sinkholes, and ground subsidence. Studying geohazards involves understanding the geological processes that trigger them, developing techniques for monitoring and predicting geohazard occurrences, and mitigating their impacts on society.
- Water Resources: Water is a critical resource for life on Earth, and the study of water resources is an important topic within Earth Science. This can involve studying the hydrological cycle, surface water and groundwater systems, water quality, water availability, and water management strategies to ensure sustainable use and protection of this vital resource.
- Geological History: Studying the geological history of the Earth provides insights into its evolution over millions of years, including the formation of rocks, minerals, mountains, and the development of ancient environments and ecosystems. It involves investigating the fossil record, stratigraphy, paleoclimatology, and other methods to reconstruct the Earth’s history and understand its geological processes and changes over time.
- Environmental Conservation: Earth Science also encompasses research on environmental conservation, including the study of ecosystems, biodiversity, and the impacts of human activities on the environment. This includes developing strategies for conserving and restoring natural resources, protecting endangered species, and managing ecosystems for sustainable use.
All areas of Earth Science contribute to our understanding of the Earth and its systems, and collectively help address important environmental challenges facing our planet.
More Read






